After working in product for a number of years, and building up your knowledge and experience, what’s the next step? Is it time to move into product leadership? And what does that even look like?
In April, it was great to be joined by Chris Holmes (VP of Product at IntelligenceBank) to share some of his experiences and perspectives, with lots of familiar (and new) faces in person, and with just as many online, including a couple of special visitors reaching us from as far as Germany and London!
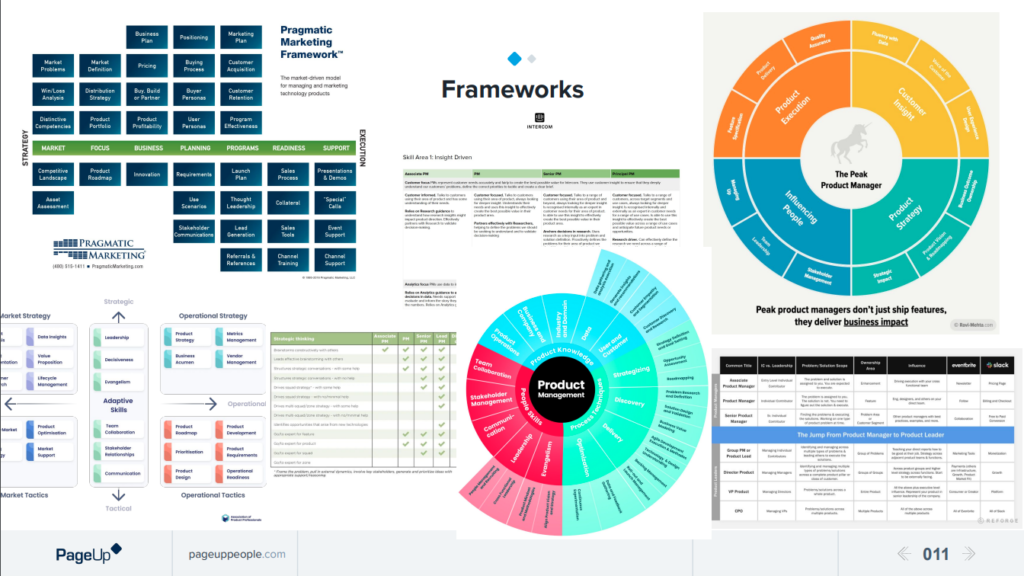
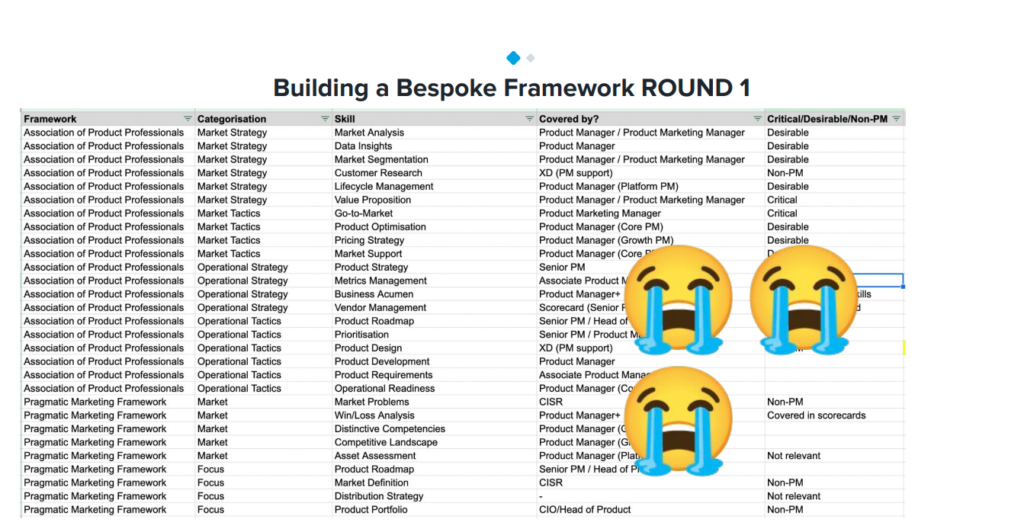
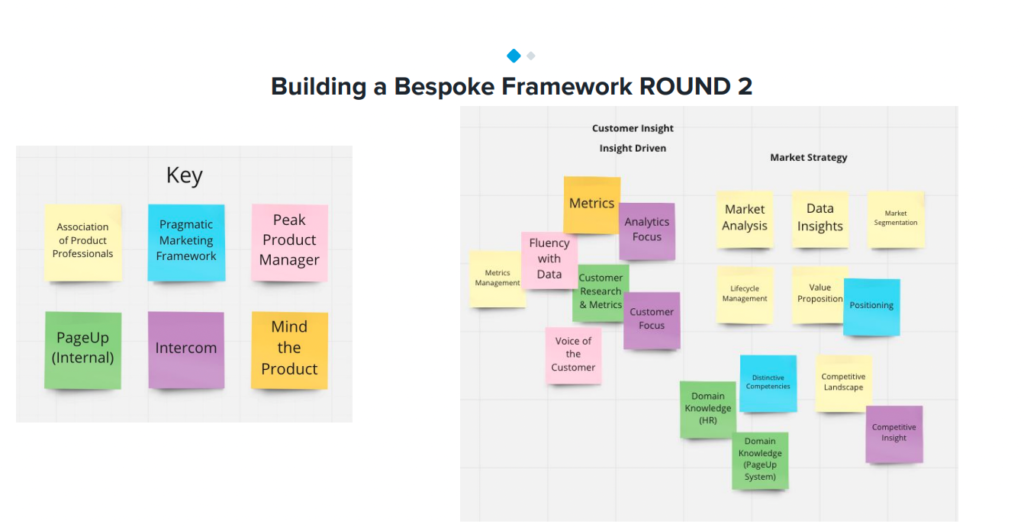
The Product Leadership Pathway
Senior Product Manager
Generally the first step to leadership is taking on a senior role. This can mean different things in different organisations. From looking after more critical products or projects, with more attention from stakeholders, to possibly having some people under you to manage, such as associate product managers, product managers or business analysts.
Head of Product / Product Director / Vice President of Product
What are the differences in all these titles? There is some localisation, with Head ofs being more popular in Australia, and Vice Presidents being more prevalent in the US. Regardless, as you progress to this level, you’ll typically be managing a team of product managers, and be more responsible for the strategy and its execution. The scale continues to get bigger.
Chief Product Officer
As you move up, the scope (and scale) continues to change, with more complex products or multiple products. You become completely responsible for end to end growth of the product, covering acquisition, retention, revenue, etc – the full range of AARRR metrics!
Common Myths about moving into Product Leadership
You can use the skills that you use today
Moving into product leadership requires a new set of skills to scale whatever success you may have experienced as an individual contributor. Coaching, developing and letting go of some of the product processes, and allowing your team to occasionally stumble and to find their own way.
You get to make all the calls
Although you may be able to use your seniority to veto decisions and make your own calls, you should proceed with caution. Much of product management is about aligning your stakeholders and to ensure everybody is pulling in the same direction. In the long run, you want to empower your team to be able to make those good decisions.
Product leadership is the next step in your product career
If you enjoy solving product problems, testing different hypotheses, and talking to customers, there is nothing wrong with continuing to be a product manager. You don’t have to move into a leadership position. Is it really something you want to do? The question you need to ask yourself is:
Do you want to manage people, or manage products?
An Average Day in the life of a Product Leader
Communicating with stakeholders
Much of Chris’ time is spent connecting and listening to various stakeholders. From aligning with the leadership team, to hearing from other team members about what’s happening in the market, and managing any escalations and issues that come up. It is extremely important to make sure everybody is on board with the strategy. Ultimately, creating relationships with other areas so you can tackle problems together.
Managing expectations
Part of being a product manager is saying no to people and their ideas. Make sure you get a load of practice, because as you move up, this only continues. Except, now it will commonly be to Head of Departments or even the CEO.
Strategy
Whether you’re setting the strategy, evolving the existing strategy or changing the direction of the strategy, you will need to constantly work with your colleagues to ensure you have alignment. For established products, you’ll need to understand where your product sits, and how you want to approach things.
Coaching and development
Make sure you allocate time to spend time with your team. Time to hear feedback from people they’ve worked with, or others in the team. How they’ve tackled problems. To give some insight, Chris usually spends about 50% of his time coaching his team, from going through the General Assembly content that he used to teach, and now with fortnightly dedicated product time.
If you need to build up a team, get ready to spend plenty of time in recruitment.
Dealing with something on fire
Like any company, there will be issues that arise. However, as a product leader, your role will evolve from putting them out yourself, to dealing with your team, so that they can resolve things themselves.
This might all seem like the regular stuff for any product manager, however as you become more senior, it becomes more about scale, having a broader viewpoint, and how you deal with things, whether that is shifting resources, changing scope, or helping to get decisions made. Remember to keep a cool head, and act like a leader.
The Essentials of Product Leadership
Being a product advocate
There will always be elements and nuance between different products and industries, and things will never always be set up perfectly. However, the key should be about setting your team and yourself up to be empowered to make the right decisions, and to deliver the most value for customers at scale.
As a product leader, you will have a seat at the table with marketing, sales, customer success and other teams, who will be pushing for certain things, which gives you the opportunity to bring the end-user to the forefront, and advocate for them.
Establishing processes for your team to validate things at different stages of the product development lifecycle, from opportunities and discovery, etc. And then giving them the space to actually do it, and not just moving through an existing roadmap of features that have been prioritised from above.
Communication
Like all product roles, communication is key.
- Identifying your stakeholders, and understanding who will need high frequency-high touch, and who will need low frequency-low touch, and working with them to get on the bus.
- Also another great opportunity to empower your team to connect with other stakeholders (including senior ones), allowing them to gain visibility, and set them on the path to success.
- Lastly, make time for your team, so you can see how they’re going, where they are struggling and what support they may need.
Know your Market
Recognise where your product sits and who is your addressable market? If you need to move into another market, what does that look like? What are the similarities where you can leverage existing solutions? What are the differences where new strategies will need to be developed?
Understanding your team
What are your team’s strengths and weaknesses? What motivates them? Be sure to carve out time so that you can understand them. Where can you leverage their strengths? Where do they need more development and guidance? A good chance to match their responsibilities and goals back to their KPIs.
Moments of Truth
Define what success looks like
It’s essential that you know how your product is performing, as you will be the one reporting back on how successful your product is.
Make sure your team knows what success looks like. Set it up together with them, so that when decisions are made, it can be linked back to success.
Sometimes, with established products, there may be an abundance of data available. However, if they are not driving any decisions, you may need to go back to basics:
- Define the core feature and actions.
- Do some historical analysis and overlay them with metrics such as Customer Success, CSAT, NPS, etc.
- Baseline – if you don’t know where you are today, how can you measure any change?
Culture
It is not uncommon to find companies that are stuck in the build trap – who only focus on delivery and not much else. These companies with a poor product-practice can be difficult to change. They may be supportive at first, but it takes time, and constant reinforcement to show the value of product thinking.
Talk to some customers. Showcase the findings. Bring people into the process, and get them hooked on the insights.
If you’re going to move something into development for a few months, and spend so much time and effort, it really is worth taking some time to sort out the basics first, validating customer desire, and that the solutions will make a difference.

Setting Up your Team (and yourself) for Success
- Set clear goal and objectives;
- Process and systems;
- Make time for coaching and development;
- Prioritise ruthlessly; and
- Get out of the way.
Lessons Learnt
Delivery can be one of the hardest items to control when moving into product leadership.
- Use your influence to change the direction of the product.
- As you scale, there is usually a (false) expectation to deliver faster.
- When faced with time pressures to deliver, you can consider changing resourcing, or scope.
- Consider how you will disseminate information to stakeholders. Create different rituals to bring people into the tent, and involve your team to help spread the load. This will also help remove yourself as a bottleneck for information and future updates.
Spend time with customers.
- Just because you move into a product leadership position, doesn’t mean you should stop hearing from your customers directly.
- Reserve time to listen to your customers, so you can understand how they are using the product. What do you really like about the product? What are the gaps?
- Bring a Product Manager, so you are not listening to feedback in isolation.
Empower your team
- Create a safe space (with appropriate guardrails) for your team to try things and learn.
- Have regular check-ins, so you can hear feedback from them, or their stakeholders.
- Get them to present to others and senior leaders, so they can craft their style, and also build their credibility.
Don’t try to change everything at once (or by yourself).
- Just like a product, there are an endless number of things you can do or change.
- Develop a strategy and be realistic of what you can achieve.
- Where are you now, where do you want to get to, and what are the steps to take to get there?
- Don’t just start trying to fix everything, and burn yourself out.
Get help!
- It can be overwhelming when you are new to the role, with large amounts of information to learn, and stakeholders approaching from all directions.
- Network with other product people and leaders, and see how they approach things.
- Get a product mentor for advice.
Planning the Move into a Leadership Role
- Look for opportunities for growth in your current role.
- Act like a leader.
- Be comfortable with uncertainty.
About our Speaker
Chris Holmes is a digital delivery and product specialist with over 10 years experience launching and managing products for companies including Jetstar, SWEAT and Origin Energy. Chris has a strong passion for customer experience and driving change through technology, and central to his product management philosophy is a focus on ensuring collaboration to deliver results.
Chris is now VP of Product at IntelligenceBank, a marketing operations SaaS platform that delivers applications for management of digital assets, creative approvals and compliance, marketing project management and creative distribution.
Further resources
- https://www.askable.com/ for customer research
- More about Dave McClure’s Pirate Metrics
- More insights about Product Leadership from our Ask Me Anything session.
- More insights about Hiring in Product from another of our Ask Me Anything sessions.
Thank You
Thank you again to Chris Holmes for sharing some of his experience and insights, to Nosh for helping to organise, to Aaron and PageUp for hosting, and to our Zoom sponsor A Cloud Guru (Pluralsight).